Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday, 18 June 1815, near Waterloo in Belgium, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands at the time. A French army under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte was defeated by two of the armies of the Seventh Coalition: A British-led coalition consisting of units from the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Hanover, Brunswick and Nassau, under the command of the Duke of Wellington, referred to by many authors as the Anglo-allied army or Wellington's army, and a Prussian army under the command of Field Marshal von Blücher, referred also as Blücher's army. The battle marked the end of the Napoleonic Wars.
Upon Napoleon's return to power in March 1815, many states that had opposed him formed the Seventh Coalition and began to mobilise armies. Wellington and Blücher's armies were cantoned close to the northeastern border of France. Napoleon planned to attack them separately in the hope of destroying them before they could join in a coordinated invasion of France with other members of the coalition. On 16 June, Napoleon successfully attacked the bulk of the Prussian army at the Battle of Ligny with his main force, causing the Prussians to withdraw northwards on 17 June, but parallel to Wellington and in good order. Napoleon sent a third of his forces to pursue the Prussians, which resulted in the separate Battle of Wavre with the Prussian rear-guard on 18–19 June, and prevented that French force from participating at Waterloo. Also on 16 June, a small portion of the French army contested the Battle of Quatre Bras with the Anglo-allied army. The Anglo-allied army held their ground on 16 June, but the withdrawal of the Prussians caused Wellington to withdraw north to Waterloo on 17 June.
Upon learning that the Prussian army was able to support him, Wellington decided to offer battle on the Mont-Saint-Jean escarpment across the Brussels road, near the village of Waterloo. Here he withstood repeated attacks by the French throughout the afternoon of 18 June, aided by the progressively arriving Prussians who attacked the French flank and inflicted heavy casualties. In the evening Napoleon assaulted the Anglo-allied line with his last reserves, the senior infantry battalions of the French Imperial Guard. With the Prussians breaking through on the French right flank, the Anglo-allied army repulsed the Imperial Guard, and the French army was routed.
Waterloo was the decisive engagement of the Waterloo Campaign and Napoleon's last. According to Wellington, the battle was "the nearest-run thing you ever saw in your life". Napoleon abdicated four days later, and coalition forces entered Paris on 7 July. The defeat at Waterloo ended Napoleon's rule as Emperor of the French and marked the end of his Hundred Days return from exile. This ended the First French Empire and set a chronological milestone between serial European wars and decades of relative peace, often referred to as the Pax Britannica. The battlefield is located in the Belgian municipalities of Braine-l'Alleud and Lasne, about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south of Brussels, and about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) from the town of Waterloo. The site of the battlefield today is dominated by the monument of the Lion's Mound, a large artificial hill constructed from earth taken from the battlefield itself; the topography of the battlefield near the mound has not been preserved.

Prelude
On 13 March 1815, six days before Napoleon reached Paris, the powers at the Congress of Vienna declared him an outlaw. Four days later, the United Kingdom, Russia, Austria, and Prussia mobilised armies to defeat Napoleon. Critically outnumbered, Napoleon knew that once his attempts at dissuading one or more members of the Seventh Coalition from invading France had failed, his only chance of remaining in power was to attack before the coalition mobilised.
Had Napoleon succeeded in destroying the existing coalition forces south of Brussels before they were reinforced, he might have been able to drive the British back to the sea and knock the Prussians out of the war. Crucially, this would have bought him time to recruit and train more men before turning his armies against the Austrians and Russians.
An additional consideration for Napoleon was that a French victory might cause French-speaking sympathisers in Belgium to launch a friendly revolution. Also, coalition troops in Belgium were largely second-line, as many units were of dubious quality and loyalty, and most of the British veterans of the Peninsular War had been sent to North America to fight in the War of 1812.
The initial dispositions of British commander Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, were intended to counter the threat of Napoleon enveloping the Coalition armies by moving through Mons to the south-west of Brussels. This would have pushed Wellington closer to the Prussian forces, led by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, but might have cut Wellington's communications with his base at Ostend. In order to delay Wellington's deployment, Napoleon spread false intelligence which suggested that Wellington's supply chain from the channel ports would be cut.
By June, Napoleon had raised a total army strength of about 300,000 men. The force at his disposal at Waterloo was less than one third that size, but the rank and file were nearly all loyal and experienced soldiers. Napoleon divided his army into a left wing commanded by Marshal Ney, a right wing commanded by Marshal Grouchy and a reserve under his command (although all three elements remained close enough to support one another). Crossing the frontier near Charleroi before dawn on 15 June, the French rapidly overran Coalition outposts, securing Napoleon's "central position" between Wellington's and Blücher's armies. He hoped this would prevent them from combining, and he would be able to destroy first the Prussian's army, then Wellington's.

Only very late on the night of 15 June was Wellington certain that the Charleroi attack was the main French thrust. In the early hours of 16 June, at the Duchess of Richmond's ball in Brussels, he received a dispatch from the Prince of Orange and was shocked by the speed of Napoleon's advance. He hastily ordered his army to concentrate on Quatre Bras, where the Prince of Orange, with the brigade of Prince Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar, was holding a tenuous position against the soldiers of Ney's left wing.
Ney's orders were to secure the crossroads of Quatre Bras, so that he could later swing east and reinforce Napoleon if necessary. Ney found the crossroads of Quatre Bras lightly held by the Prince of Orange, who repelled Ney's initial attacks but was gradually driven back by overwhelming numbers of French troops. First reinforcements, and then Wellington arrived. He took command and drove Ney back, securing the crossroads by early evening, too late to send help to the Prussians, who had already been defeated.
Meanwhile on 16 June, Napoleon attacked and defeated Blücher's Prussians at the Battle of Ligny using part of the reserve and the right wing of his army. The Prussian centre gave way under heavy French assaults, but the flanks held their ground. The Prussian retreat from Ligny went uninterrupted and seemingly unnoticed by the French. The bulk of their rearguard units held their positions until about midnight, and some elements did not move out until the following morning, ignored by the French.
Crucially, the Prussians did not retreat to the east, along their own lines of communication. Instead, they, too, fell back northwards—parallel to Wellington's line of march, still within supporting distance and in communication with him throughout. The Prussians rallied on Bülow's IV Corps, which had not been engaged at Ligny and was in a strong position south of Wavre.

With the Prussian retreat from Ligny, Wellington's position at Quatre Bras was untenable. The next day he withdrew northwards, to a defensive position he had reconnoitred the previous year—the low ridge of Mont-Saint-Jean, south of the village of Waterloo and the Sonian Forest.
Napoleon, with the reserves, made a late start on 17 June and joined Ney at Quatre Bras at 13:00 to attack Wellington's army but found the position empty. The French pursued Wellington's retreating army to Waterloo; however, due to bad weather, mud and the head start that Napoleon's tardy advance had allowed Wellington, apart from a cavalry action at Genappe, there was no substantial engagement.
Before leaving Ligny, Napoleon had ordered Grouchy, who commanded the right wing, to follow up the retreating Prussians with 33,000 men. A late start, uncertainty about the direction the Prussians had taken, and the vagueness of the orders given to him, meant that Grouchy was too late to prevent the Prussian army reaching Wavre, from where it could march to support Wellington. More importantly, the heavily outnumbered Prussian rear-guard was able to use the River Dyle to enable a savage and prolonged action to delay Grouchy.
As 17 June drew to a close, Wellington's army had arrived at its position at Waterloo, with the main body of Napoleon's army following. Blücher's army was gathering in and around Wavre, around 8 miles (13 km) to the east of the town. Early on the morning of the 18th, Wellington received an assurance from Blücher that the Prussian army would support him. He decided to hold his ground and give battle.

Armies
The French army of around 69,000 consisted of 48,000 infantry, 14,000 cavalry, and 7,000 artillery with 250 guns. Napoleon had used conscription to fill the ranks of the French army throughout his rule, but he did not conscript men for the 1815 campaign. His troops were mainly veterans with considerable experience and a fierce devotion to their Emperor. The cavalry in particular was both numerous and formidable, and included fourteen regiments of armoured heavy cavalry, and seven of highly versatile lancers who were armed with lances, sabres and firearms.
However, as the army took shape, French officers were allocated to units as they presented themselves for duty, so that many units were commanded by officers the soldiers didn't know, and often didn't trust. Crucially, some of these officers had little experience in working together as a unified force, so that support for other units was often not given.
The French army was forced to march through rain and black coal-dust mud to reach Waterloo, and then to contend with mud and rain as it slept in the open. Little food was available for the soldiers, but nevertheless the veteran French soldiers were fiercely loyal to Napoleon.
Wellington later said that he had "an infamous army, very weak and ill-equipped, and a very inexperienced Staff". His troops consisted of 67,000 men: 50,000 infantry, 11,000 cavalry, and 6,000 artillery with 150 guns. Of these, 25,000 were British, with another 6,000 from the King's German Legion (KGL). All of the British Army troops were regular soldiers, but only 7,000 of them were Peninsular War veterans. In addition, there were 17,000 Dutch and Belgian troops, 11,000 from Hanover, 6,000 from Brunswick, and 3,000 from Nassau.

Many of the troops in the Coalition armies were inexperienced. The Dutch army had been re-established in 1815, following the earlier defeat of Napoleon. With the exception of the British and some from Hanover and Brunswick who had fought with the British army in Spain, many of the professional soldiers in the Coalition armies had spent some of their time in the French army or in armies allied to the Napoleonic regime. The historian Alessandro Barbero states that in this heterogeneous army the difference between British and foreign troops did not prove significant under fire.
Wellington was also acutely short of heavy cavalry, having only seven British and three Dutch regiments. The Duke of York imposed many of his staff officers on Wellington, including his second-in-command the Earl of Uxbridge. Uxbridge commanded the cavalry and had carte blanche from Wellington to commit these forces at his discretion. Wellington stationed a further 17,000 troops at Halle, 8 miles (13 km) away to the west. They were mostly composed of Dutch troops under the Prince of Orange's younger brother Prince Frederick of the Netherlands. They were placed as a guard against any possible wide flanking movement by the French forces, and also to act as a rearguard if Wellington was forced to retreat towards Antwerp and the coast.
The Prussian army was in the throes of reorganisation. In 1815, the former Reserve regiments, Legions, and Freikorps volunteer formations from the wars of 1813–1814 were in the process of being absorbed into the line, along with many Landwehr (militia) regiments. The Landwehr were mostly untrained and unequipped when they arrived in Belgium. The Prussian cavalry were in a similar state. Its artillery was also reorganising and did not give its best performance—guns and equipment continued to arrive during and after the battle.
Offsetting these handicaps, the Prussian Army had excellent and professional leadership in its General Staff organisation. These officers came from four schools developed for this purpose and thus worked to a common standard of training. This system was in marked contrast to the conflicting, vague orders issued by the French army. This staff system ensured that before Ligny, three-quarters of the Prussian army concentrated for battle with 24 hours' notice.
After Ligny, the Prussian army, although defeated, was able to realign its supply train, reorganise itself, and intervene decisively on the Waterloo battlefield within 48 hours. Two and a half Prussian army corps, or 48,000 men, were engaged at Waterloo; two brigades under Bülow, commander of IV Corps, attacked Lobau at 16:30, while Zieten's I Corps and parts of Pirch I's II Corps engaged at about 18:00.

Battlefield
The Waterloo position was a strong one. It consisted of a long ridge running east–west, perpendicular to, and bisected by, the main road to Brussels. Along the crest of the ridge ran the Ohain road, a deep sunken lane. Near the crossroads with the Brussels road was a large elm tree that was roughly in the centre of Wellington's position and served as his command post for much of the day. Wellington deployed his infantry in a line just behind the crest of the ridge following the Ohain road.
Using the reverse slope, as he had many times previously, Wellington concealed his strength from the French, with the exception of his skirmishers and artillery. The length of front of the battlefield was also relatively short at 2.5 miles (4 km). This allowed Wellington to draw up his forces in depth, which he did in the centre and on the right, all the way towards the village of Braine-l'Alleud, in the expectation that the Prussians would reinforce his left during the day.
In front of the ridge, there were three positions that could be fortified. On the extreme right were the château, garden, and orchard of Hougoumont. This was a large and well-built country house, initially hidden in trees. The house faced north along a sunken, covered lane (usually described by the British as "the hollow-way") along which it could be supplied. On the extreme left was the hamlet of Papelotte.
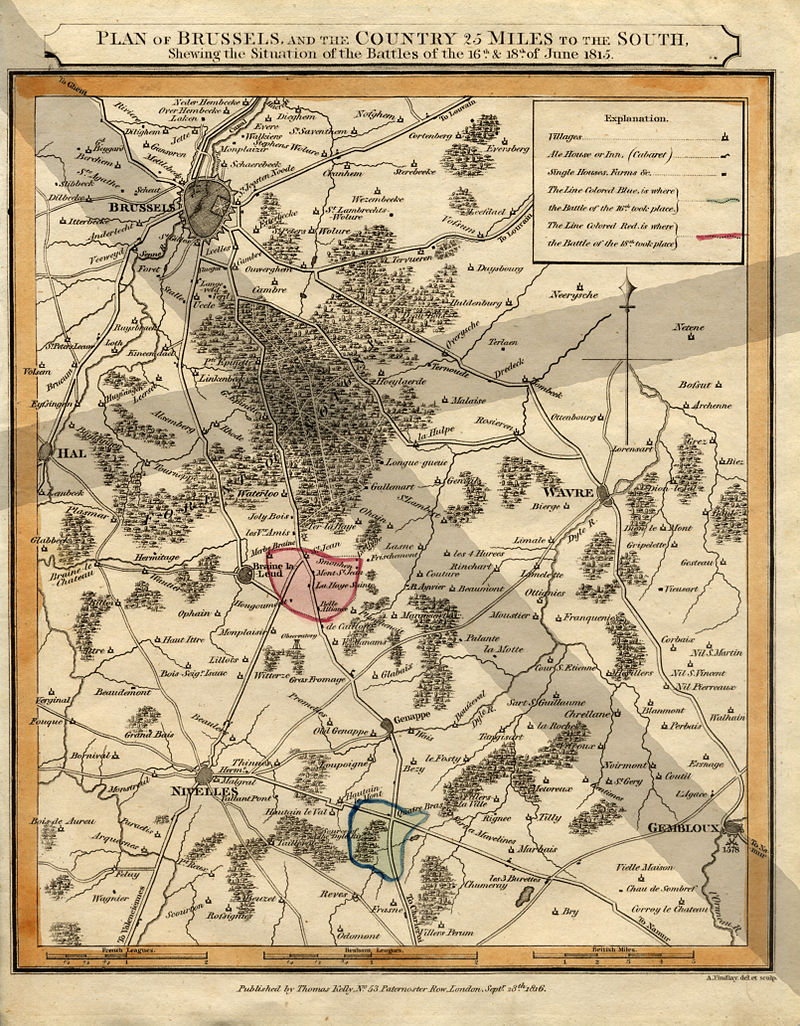
Both Hougoumont and Papelotte were fortified and garrisoned, and thus anchored Wellington's flanks securely. Papelotte also commanded the road to Wavre that the Prussians would use to send reinforcements to Wellington's position. On the western side of the main road, and in front of the rest of Wellington's line, was the farmhouse and orchard of La Haye Sainte, which was garrisoned with 400 light infantry of the King's German Legion. On the opposite side of the road was a disused sand quarry, where the 95th Rifles were posted as sharpshooters.
Wellington's forces positioning presented a formidable challenge to any attacking force. Any attempt to turn Wellington's right would entail taking the entrenched Hougoumont position. Any attack on his right centre would mean the attackers would have to march between enfilading fire from Hougoumont and La Haye Sainte. On the left, any attack would also be enfiladed by fire from La Haye Sainte and its adjoining sandpit, and any attempt at turning the left flank would entail fighting through the lanes and hedgerows surrounding Papelotte and the other garrisoned buildings on that flank, and some very wet ground in the Smohain defile.
The French army formed on the slopes of another ridge to the south. Napoleon could not see Wellington's positions, so he drew his forces up symmetrically about the Brussels road. On the right was I Corps under d'Erlon with 16,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry, plus a cavalry reserve of 4,700. On the left was II Corps under Reille with 13,000 infantry, and 1,300 cavalry, and a cavalry reserve of 4,600. In the centre about the road south of the inn La Belle Alliance were a reserve including Lobau's VI Corps with 6,000 men, the 13,000 infantry of the Imperial Guard, and a cavalry reserve of 2,000.
In the right rear of the French position was the substantial village of Plancenoit, and at the extreme right, the Bois de Paris wood. Napoleon initially commanded the battle from Rossomme farm, where he could see the entire battlefield, but moved to a position near La Belle Alliance early in the afternoon. Command on the battlefield (which was largely hidden from his view) was delegated to Ney.

Aftermath
Waterloo cost Wellington around 15,000 dead or wounded and Blücher some 7,000 (810 of which were suffered by just one unit: the 18th Regiment, which served in Bülow's 15th Brigade, had fought at both Frichermont and Plancenoit, and won 33 Iron Crosses). Napoleon's losses were 24,000 to 26,000 killed or wounded and included 6,000 to 7,000 captured with an additional 15,000 deserting subsequent to the battle and over the following days.
22 June. This morning I went to visit the field of battle, which is a little beyond the village of Waterloo, on the plateau of Mont-Saint-Jean; but on arrival there the sight was too horrible to behold. I felt sick in the stomach and was obliged to return. The multitude of carcasses, the heaps of wounded men with mangled limbs unable to move, and perishing from not having their wounds dressed or from hunger, as the Anglo-allies were, of course, obliged to take their surgeons and waggons with them, formed a spectacle I shall never forget. The wounded, both of the Anglo-allies and the French, remain in an equally deplorable state.
— Major W. E. Frye.

At 10:30 on 19 June General Grouchy, still following his orders, defeated General Thielemann at Wavre and withdrew in good order—though at the cost of 33,000 French troops that never reached the Waterloo battlefield. Wellington sent his official dispatch describing the battle to England on 19 June 1815; it arrived in London on 21 June 1815 and was published as a London Gazette Extraordinary on 22 June. Wellington, Blücher and other Coalition forces advanced upon Paris.
Napoleon announced his second abdication on 24 June 1815. In the final skirmish of the Napoleonic Wars, Marshal Davout, Napoleon's minister of war, was defeated by Blücher at Issy on 3 July 1815. Allegedly, Napoleon tried to escape to North America, but the Royal Navy was blockading French ports to forestall such a move. He finally surrendered to Captain Frederick Maitland of HMS Bellerophon on 15 July. There was a campaign against French fortresses that still held out; Longwy capitulated on 13 September 1815, the last to do so. Louis XVIII was restored to the throne of France and Napoleon was exiled to Saint Helena, where he died in 1821. The Treaty of Paris was signed on 20 November 1815.
Royal Highness, – Exposed to the factions which divide my country, and to the enmity of the great Powers of Europe, I have terminated my political career; and I come, like Themistocles, to throw myself upon the hospitality (m'asseoir sur le foyer) of the British people. I claim from your Royal Highness the protections of the laws, and throw myself upon the most powerful, the most constant, and the most generous of my enemies.
— Napoleon. (letter of surrender to the Prince Regent; translation).

Maitland's 1st Foot Guards, who had defeated the Chasseurs of the Imperial Guard, were thought to have defeated the Grenadiers, although they had only faced Chasseurs of the newly raised Middle Guard. They were nevertheless awarded the title of Grenadier Guards in recognition of their feat and adopted bearskins in the style of the Grenadiers. Britain's Household Cavalry likewise adopted the cuirass in 1821 in recognition of their success against their armoured French counterparts. The effectiveness of the lance was noted by all participants and this weapon subsequently became more widespread throughout Europe; the British converted their first light cavalry regiment to lancers in 1816, their uniforms, of Polish origin, were based on those of the Imperial Guard lancers.
Teeth of tens of thousands of dead soldiers were removed by surviving troops, locals or even scavengers who had travelled there from Britain, then used for making denture replacements in Britain and elsewhere. The so-called "Waterloo teeth" were in demand because they came from relatively healthy young men. Despite the efforts of scavengers both human and otherwise, human remains could still be seen at Waterloo a year after the battle.














0 comments
Sign in or create a free account